1D Barcodes
1 Dimensional (1D) barcodes are represented by parallel black bars and numbers. 1D barcodes are what you typically think of when you hear the word barcode. George Laurer’s UPC codes, which are typically found in retail stores, are the most common type of a 1D barcode. 1D barcodes contain a small amount of data or information that can be extracted with the use of a barcode scanner. To be exact, according to Barcodes Inc, 1D barcodes can only hold between 20-25 characters of data.
The main benefit of 1D barcodes is that the scanners for 1D barcodes are less expensive than the alternative 2D barcode scanners. The reason for this is 2D barcode scanning technology is newer and therefore more expensive. If your organization does not need to hold a large amount of information within your barcodes, 1D barcodes are the most money-wise option. Another advantage is the overall performance of the 1D barcode scanner, as it generally performs faster, has a longer scanning range, and can scan without being affected by lighting.


2D Barcodes
2 Dimensional (2D) are barcodes that represent data in a matrix of contrasting cells. The most common 2D barcode is the QR code, which is heavily used for advertising and marketing purposes. However, 2D barcodes are used for much more than advertising. Unlike 1D barcodes, 2D barcodes can contain data vertically and horizontally, which allows the barcode to contain much more information than its processor. According to Barcodes Inc, 2D barcodes can contain 2000 characters or more. They are also able to link to websites, can be used for product tracking, product identification, and more.
One of the 2D barcode include being able to scan the barcode from any direction. This makes scanning quicker and more efficient. Another benefit is only needing to scan the barcode once to collect all information. With 2D barcodes, multiple fields in your inventory system can be populated at once, versus making multiple scans with 1D barcodes. This is especially beneficial for working within a warehouse, where hundreds of scans are made a day. Another benefit is that 2D scanners have the ability to reduce the use of counterfeit items, by improving tracking of items through the supply chain. 2D barcodes can carry much more information than the 1D barcode, making products more difficult to counterfeit.
Main Differences Between 1D and 2D Barcodes
| Feature | 1D Barcode | 2D Barcode |
|---|---|---|
| Amount of data stored | 8-15 Characters | 2000+ Characters |
| Scan Position | Upright | Any |
| Read data | Horizontally | Vertically and Horizontally |
| Popular Industries | Retail, Healthcare, Manufacturing, Supply Chain, Logistics, Transportation | Marketing, Advertising, Food Services, Electronics, Automotive, Engineering, Healthcare, Manufacturing, Warehousing, Aerospace, Telecommunications |
Things to Consider When Purchasing a Barcode Scanner
There are many different types of barcode scanners on the market today, and choosing the most suitable types important for the productivity of your business. Barcode scanners are used in industrial settings, retail stores, healthcare facilities, logistics, and warehousing. Some barcode scanners are built for specific work environments, such as extreme weather or to endure rougher conditions, while others are designed for less extreme environments and and process data at a much quicker speed. This is why, in order to maximize your organization’s efficiency, it is important to know the features and functions of various barcode scanners.
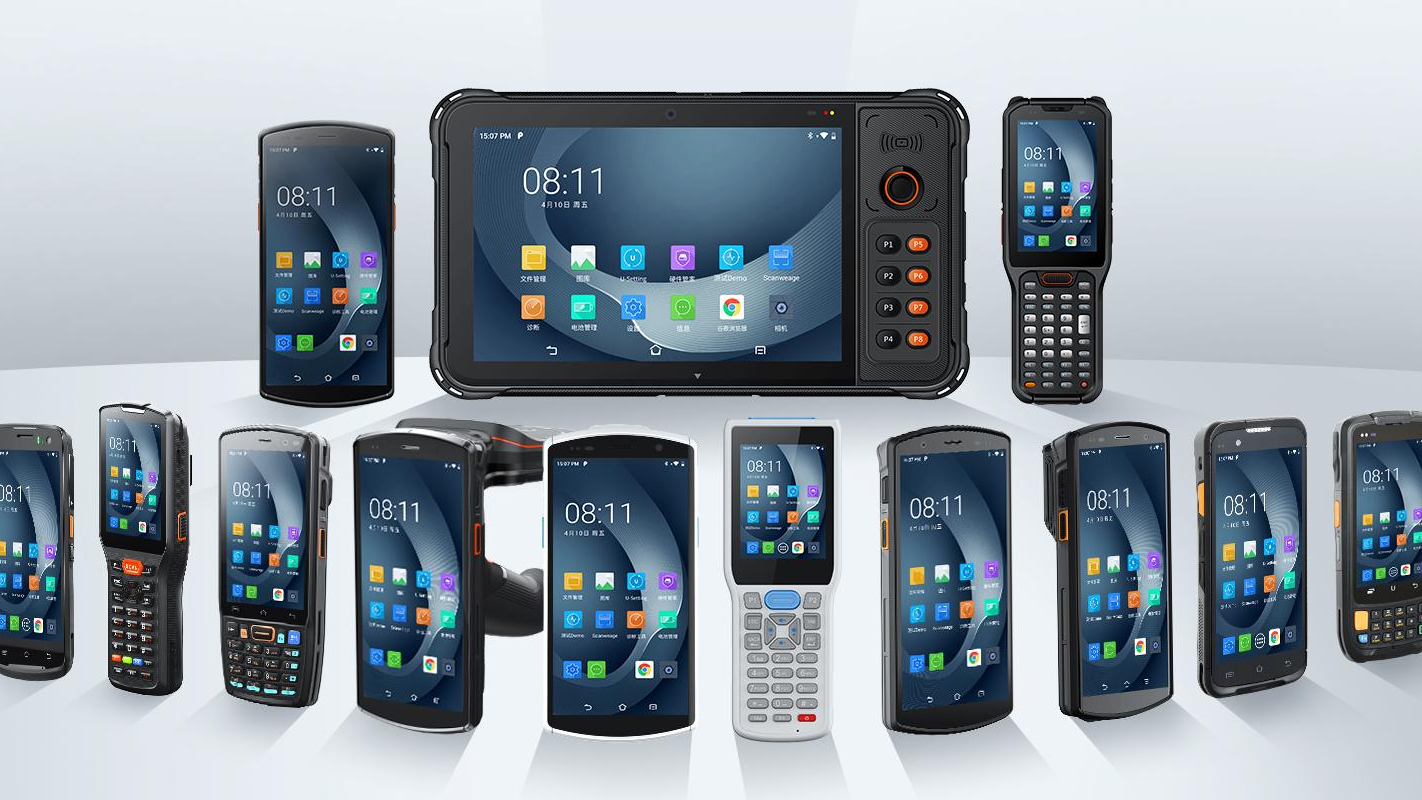
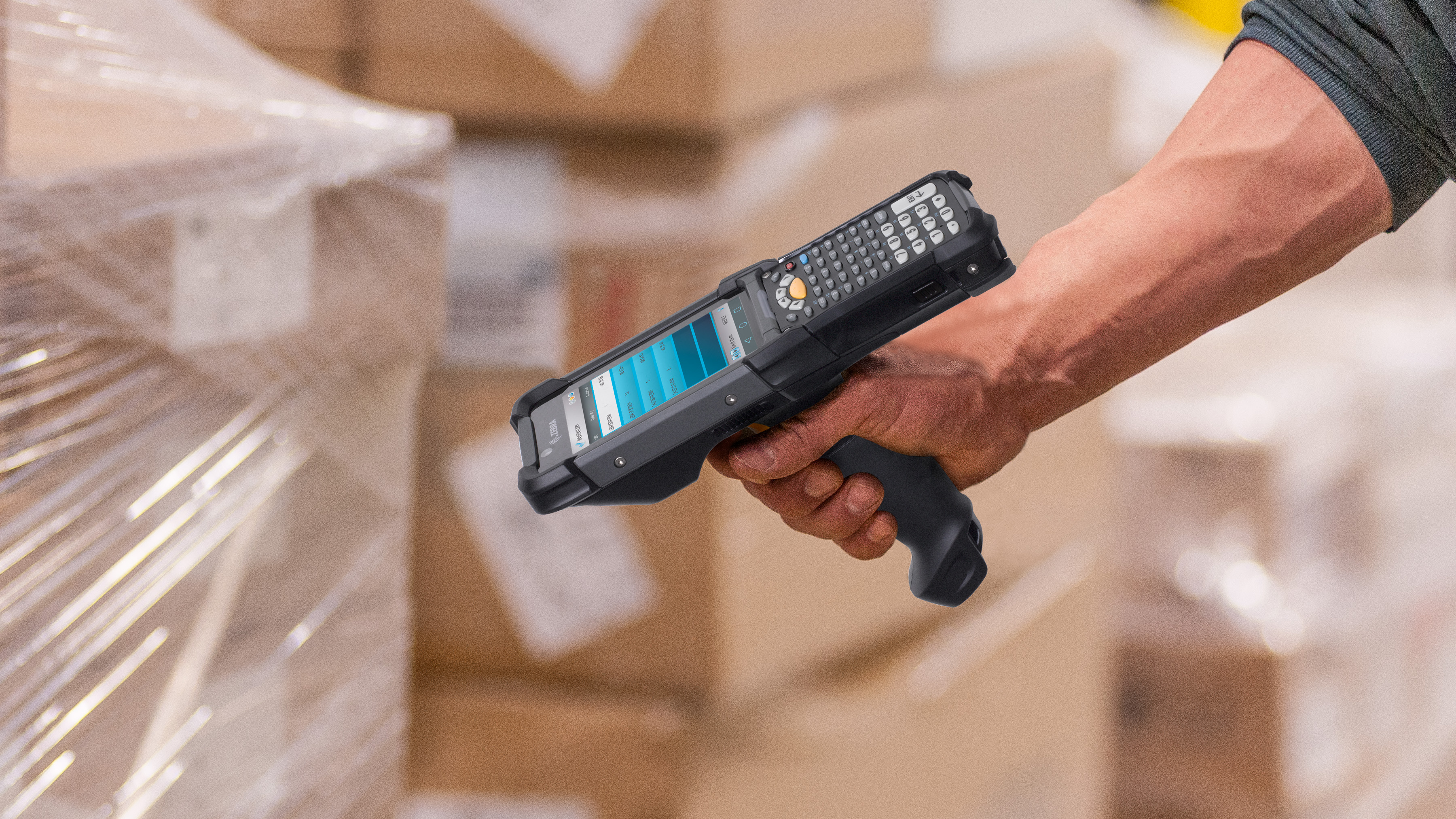
Mobile Computers
Mobile computers are fully independent computers that integrate all the necessary peripherals and interfaces needed for collecting, managing, and storing the data gathered via barcodes. Mobile computer integrates, in a small form factor, all the necessary components of a computer, such as a display, a Wi-Fi system, an operating system (Windows® or Android™), a keyboard (virtual or physical), a battery and a professional scan engine.
Mobile devices are the daily companion in activities like inventory, price check, pick and drop, assisted sales, delivery, quality control, curb-side pick-up, etc. From printed 1D and 2D barcodes, to Direct Part Marking (DPM), to Digimarc© packaging, Datalogic offers a solution for nearly every barcode reading application.
Mobile computers support enterprises to improve efficiency and reliability on all their tracking activities in every area of the company. In retail companies, they can be used on the store floor for activities such as price check, inventory, or assisted sales. In the back room, mobile devices are used for any inventory or stock rotation activities. From the docking locations where goods are unloaded, through the warehouse and other areas of the facilities, up to the point of delivery, operators use mobile computers for every bit of the process. In the manufacturing segment, they allow workers to track all the assets used for assembly or for building, and to check inventory in the warehouse. In the healthcare segment, mobile computers are becoming the trusted work companion of nurses and other operators for the bed-side point of care activities. Once the patient barcode is read, hospital staff can see all the information related to that patient.